Recently, i was tinkering around with network-related matters in qubes. And found these things to come in handy, so i am sharing them here. Not qubes-os specific, by the way.
retrieving network information with iptables & ip
In a single line that can be double-clicked and then pasted from secondary/middle-click:
{ format='' ; : '\n--- %s ---\n' ; for table in filter mangle nat raw security ; do test -z "${format?}" || printf "${format?}" "${table?}" ; sudo iptables --table $table --line-numbers -vnL ; done ;} | sed -E 's/^Chain.*$/\x1b[4m&\x1b[0m/' | sed -E 's/^num.*/\x1b[33m&\x1b[0m/' | sed -E '/([^y] )((REJECT|DROP))/s//\1\x1b[31m\3\x1b[0m/' | sed -E '/([^y] )(ACCEPT)/s//\1\x1b[32m\2\x1b[0m/' | sed -E '/([ds]pt[s]?:)([[:digit:]]+(:[[:digit:]]+)?)/s//\1\x1b[33;1m\2\x1b[0m/' | sed -E '/([[:digit:]]{1,3}\.){3}[[:digit:]]{1,3}(\/([[:digit:]]){1,3}){0,1}/s//\x1b[36;1m&\x1b[0m/g' | sed -E '/([^n] )(LOGDROP)/s//\1\x1b[33;1m\2\x1b[0m/'| sed -E 's/ LOG /\x1b[36;1m&\x1b[0m/' ; sudo ip -6 -c a s ; sudo ip -6 -c r s ; sudo ip -4 -c r s ; sudo ip -4 -c a s ;
To have “headers” for the iptables output, remove ' ; : ' from the beginning, so:
- { format='' ; : '\n
+ { format='\n
Or, split over multiple lines (semicolons (;) removed).
{
{
for table in filter mangle nat raw security
do
cmd="sudo iptables --table ${table?} --line-numbers --verbose --numeric --list"
# aka sudo iptables --line-numbers -t nat -nvL
printf '\n--- result of command: %s ---\n' "${cmd?}"
${cmd?}
done
unset cmd
} |
sed -E 's/^Chain.*$/\x1b[4m&\x1b[0m/' |
sed -E 's/^num.*/\x1b[33m&\x1b[0m/' |
sed -E '/([^y] )((REJECT|DROP))/s//\1\x1b[31m\3\x1b[0m/' |
sed -E '/([^y] )(ACCEPT)/s//\1\x1b[32m\2\x1b[0m/' |
sed -E '/([ds]pt[s]?:)([[:digit:]]+(:[[:digit:]]+)?)/s//\1\x1b[33;1m\2\x1b[0m/' |
sed -E '/([[:digit:]]{1,3}\.){3}[[:digit:]]{1,3}(\/([[:digit:]]){1,3}){0,1}/s//\x1b[36;1m&\x1b[0m/g' |
sed -E '/([^n] )(LOGDROP)/s//\1\x1b[33;1m\2\x1b[0m/' |
sed -E 's/ LOG /\x1b[36;1m&\x1b[0m/' |
: ;
sudo ip -color -family inet6 address show # aka -6 -c a s
sudo ip -color -family inet6 route show # aka -6 -c r s
sudo ip -color -family inet route show # aka -4 -c r s
sudo ip -color -family inet address show # aka -4 -c a s
}
Perhaps of interest, in man ip is documented:
-json [-pretty](usable with javascript object notation (JSON) parsing tools, for instance:jq)-oneline(allows for counting/enumerating or new-line separated iteration)
Another thing that might come in handy, is to limit addresses to the global scope, by doing:
sudo ip -c a s scope global
Combining that with -oneline/-o allows, for instance, to count amount of global interfaces (using “word” count with --lines/-l):
sudo ip -o a s scope global | wc -l
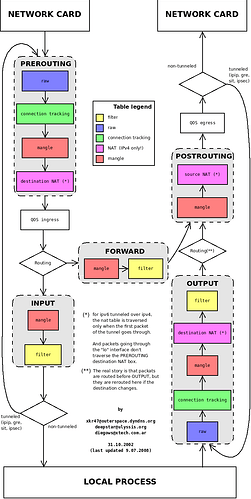
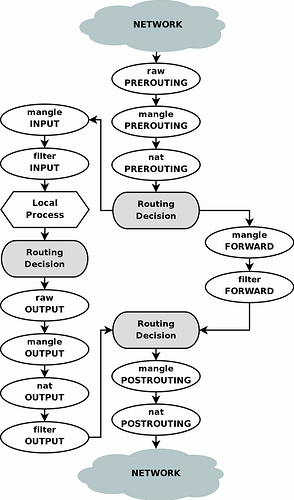
iptables visualized
There’s probably caveats, but these might be useful for understanding more of iptables/nft.
~ src: Packet flow graph
~ src: unknown
iptables migration to nft
See: iptables-translate --help.
For instance:
sudo iptables-translate --table nat --line-numbers -vnL
produces:
nft list table ip nat